題目說明
Give an efficient algorithm to determine whether or not a directed graph is singly connected.
螢幕輸入
First line is N, denotes the amount of test case, then there are Ns graph data followed by N. Second line is V, each graph data is composed of V (the number of vertices, <= 1000). Third line is E, the number of edges, it does no size limitation, then followed by Es edges which are denoted by pair of vertex (e.g., 2 4 is vertex 2->4, the first vertex number is 0 of all the vertex). Each vertex is an integer in [0, n-1], also notes that the input edge is not ordered by the start vertex.
螢幕輸出
If the input graph is singly connected, output the ”YES”, or “NO” if not.
The test case number should be printed before the answer.
Example
螢幕輸入:
2
6
8
0 1
0 4
1 2
2 0
2 1
3 2
4 5
5 4
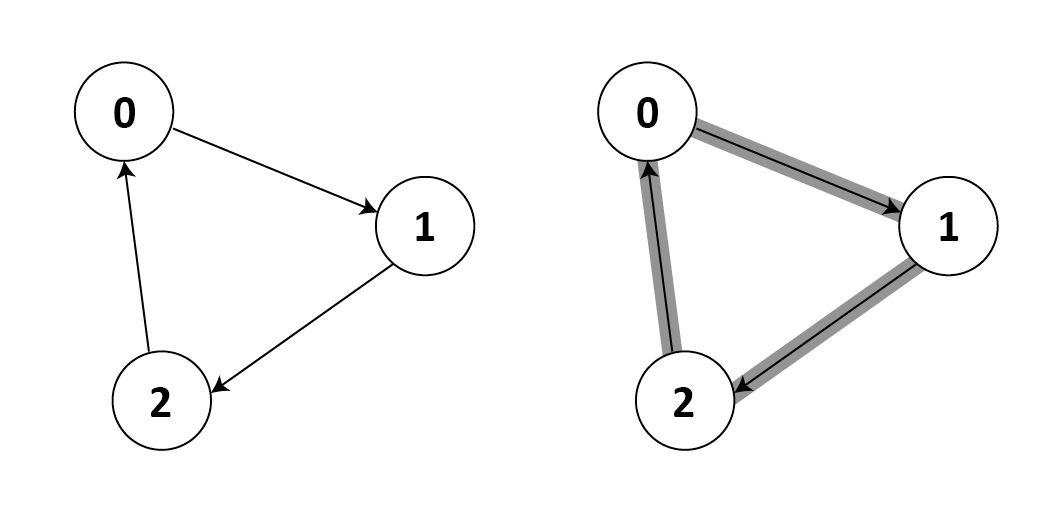
3
3
0 1
1 2
2 0
螢幕輸出:
1 NO
2 YES
題目解析
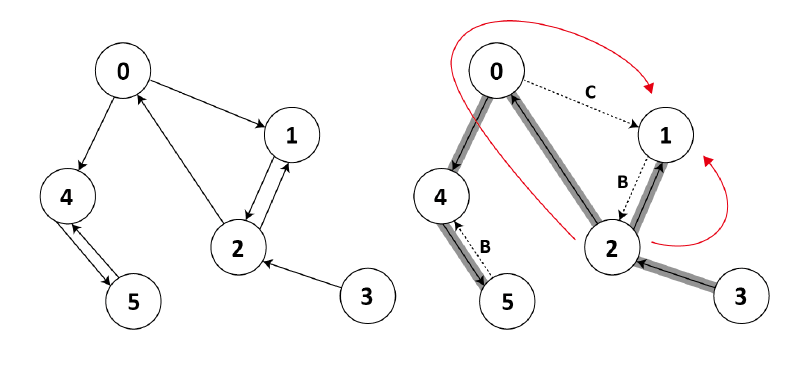
Singly Connected 的定義是任兩點只有一條路徑能到達。
於是我們利用 DFS 的特性下去處理,當如果做完的 DFS 的 Graph 中有出現 forward edge 或是 cross edge 的話,表示兩點間有其他路徑存在,則 Singly Connected 不成立。
因此我們要以每個點為 root 開始走訪過一次 DFS,看是否在每個情況中是否都不會出現 forward edge 和 cross edge,Singly Connected 才成立。
在 DFS 中提到,當我們第一次走訪 edge (u, v),我們可以從v點來得知該 edge 的特性:
- 若 v 點為白色:表示該 edge 為 tree edge(灰底線)。
- 若 v 點為灰色:表示該 edge 為 back edge(B)。
- 若 v 點為黑色:表示該 edge 為 forward(F)或 cross(C)edge。
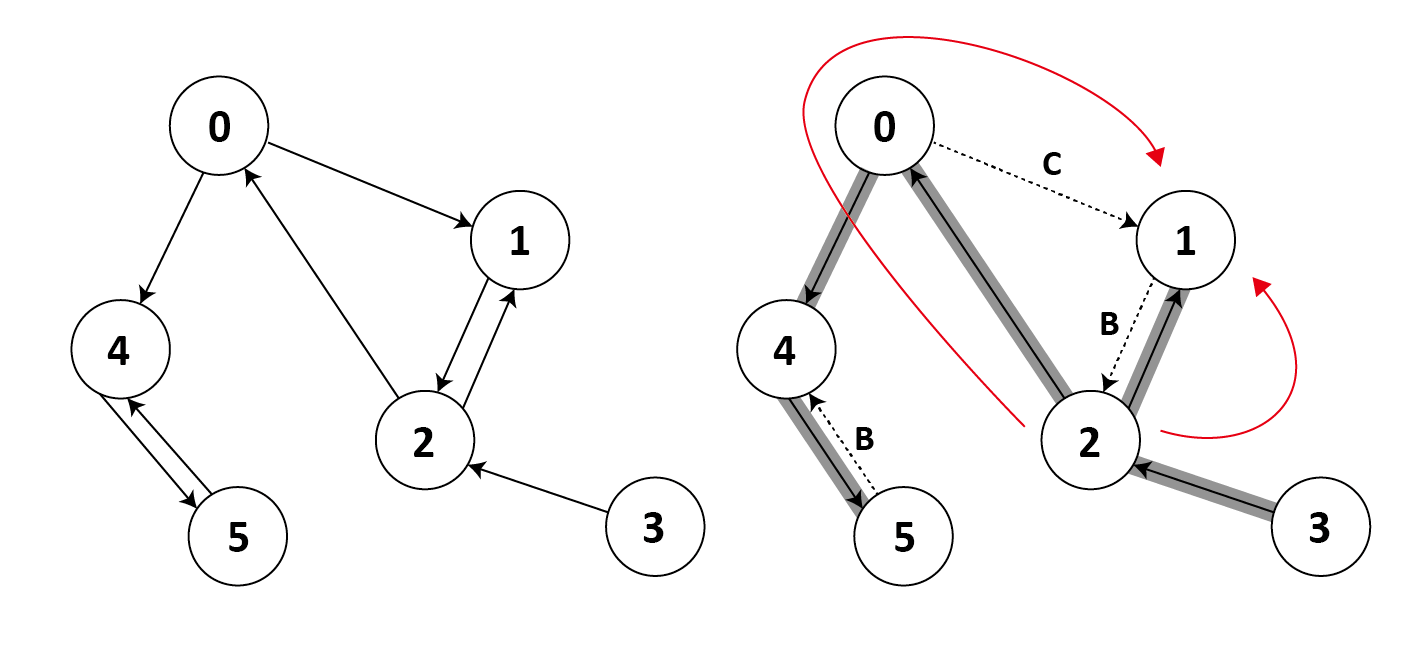
因此我們知道如何判斷 Graph 中是否有 forward edge 或是 cross edge,我們稍微修改基本 DFS 的流程,當我們在走訪該點所連接的其他點的過程中,如果發現點是白色的話,我們會紀錄 parent 和再呼叫一次 DFS Visit。
在這裡我們加上另一種情況,也就是用來判斷是否為 forward 或 cross edge 的情況,當點是黑色的話,我們回傳 FALSE,並中斷遞迴回到主程式,加快程式。
程式碼
// main.cpp
// Student ID: B10615043
// Date: May 30, 2019
// Last Update: May 30, 2019
// Problem statement: This C++ program for singly connected problem.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int color = 0; // 0 = white; 1 = gray; 2 = black;
int parent = -1; // -1 = NULL;
int discover = 0; // discover time
int finish = 0; // finish time
vector<int> adj; // adjacencyList
};
bool DFS_Visit(node* G, int uIndex, int &time);
int main()
{
int N;
// input total case number
while (cin >> N)
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
// flag to record this graph singly connected or not
bool singly = true;
int V;
// input Vertex amount
cin >> V;
// create Vector list
node *list = new node[V];
int E;
// input Edge amount
cin >> E;
for (int j = 0; j < E; j++)
{
int a, b;
// input connect vertex info to adjacency list
cin >> a >> b;
list[a].adj.push_back(b);
}
int time = 0;
// consider all vertex begin to DFS condition
for (int j = 0; j < V; j++)
{
// reset all vertex info but adjacency list
for (int k = 0; k < V; k++)
{
list[k].color = 0;
list[k].parent = -1;
list[k].finish = 0;
list[k].discover = 0;
}
// call DFS_Visit Function to determine singly connected
singly = DFS_Visit(list, j, time);
// if already not singly connected break the loop
if (singly == false) break;
}
// output case number and singly connect or not
if (singly) cout << i + 1 << " YES" << endl;
else cout << i + 1 << " NO" << endl;
// delete list to free memory
delete[] list;
}
}
return 0;
}
// Based on Slide Page 45 DFS-VISIT(G, u)
bool DFS_Visit(node* G, int u, int & time)
{
// while vertex u has just discovered
time = time + 1;
G[u].discover = time;
// set the color white to gray
G[u].color = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < G[u].adj.size(); i++)
{
// explore edge (u, v)
int v = G[u].adj[i];
// if edge is tree edge
if (G[v].color == 0)
{
// set parent and go on DFS-Visit
G[v].parent = u;
// if return false then also return false to speed up program
if (!DFS_Visit(G, v, time)) return false;
}
// if edge is forward or cross edge then return false
else if (G[v].color == 2)
{
return false;
}
}
// blacken u, it is finished
G[u].color = 2;
time = time + 1;
G[u].finish = time;
// success DFS visit(G, u) no encounter forward or cross edge return true
return true;
}
Pseudo code
// Based on Slide Page 45 DFS-VISIT(G, u)
bool DFS_Visit(node* G, int u, int & time)
// while vertex u has just discoverd
time = time + 1
G[u].discover = time
// set the color white to gray
G[u].color = GRAY
for each v in G[u].adj[]
// if edge is tree edge
if (G[v].color == WHITE)
// set parent and go on DFS-Visit
G[v].parent = u
// if return false then also return false to speed up program
if (!DFS_Visit(G, v, time)) return false
end if
// if edge is forward or cross edge then return false
else if (G[v].color == 2)
return false
end if
// blacken u, it is finished
G[u].color = BLACK
time = time + 1
G[u].finish = time
// success DFS visit(G, u) no encounter forward or cross edge return true
return true